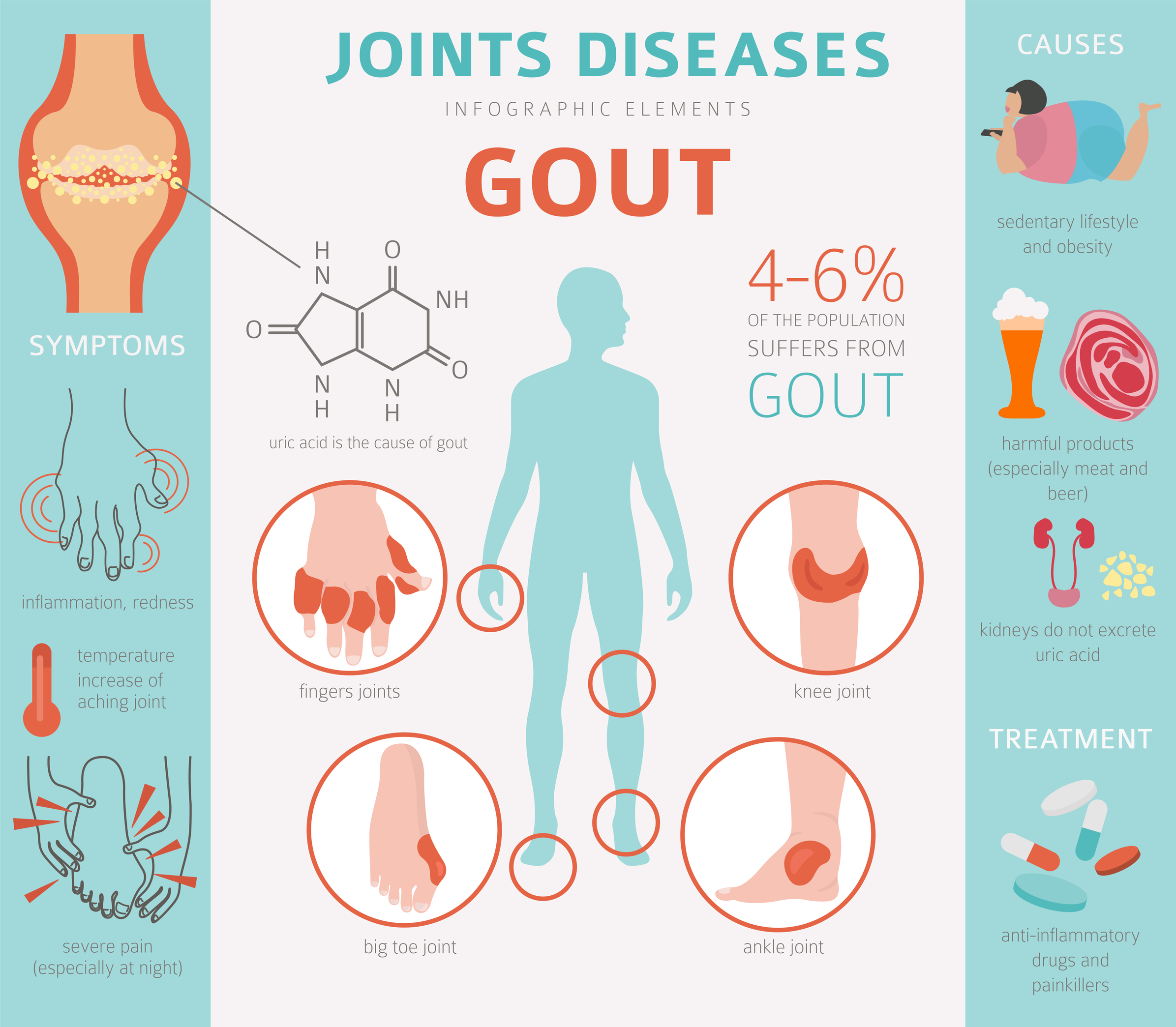
What are causes of gout?
Uric acid is generated as we metabolize the food we eat and as the body's tissues are broken down during normal cell turnover. Some people with gout generate too much uric acid (10% of those affected) and are medically referred to as "over-producers." Other people with gout do not effectively eliminate their uric acid into the urine (90%) and are medically referred to as "under-excreters."
What are gout factors?
The genes that we inherit, male gender, kidney function, and nutrition (alcoholism, obesity) play key roles in the development of gout. Gout is not contagious.
- If your parents have gout, then you have a 20% chance of developing it.
- British people are five times more likely to develop gout than others.
- American blacks, but not African blacks, are more likely to have gout than other populations.
- Post-pubertal males are at increased risk for gout compared with women.
- People with insufficient kidney function are at increased risk for gout.
- Intake of alcoholic beverages, especially beer, increases the risk for gout.
- Diets rich in red meats, internal organs, yeast, shellfish, and oily fish increase the risk for gout.
- Uric acid levels increase at puberty in men and at menopause in women, so men first develop gout at an earlier age (after puberty) than do women (after menopause). Gout in premenopausal women is distinctly unusual.